How to contribute
Contributions are very welcome. Specially roles. If you implement a role that you think others might be using, please contribute.
To contribute head to opps's github page, fork it and create a pull request.
We strive to keep the internal quality of opps to the best that we can; Therefore, it's very important to keep some things in mind when contributing with code for opps:
-
Test everything you can, with automated tests. If possible, please develop code with TDD. If you're having a hard time building tests, don't hesitate to ask for help in the opps mailing list. We are happy to help you keep your code well-covered by tests;
-
When writing actual code, follow the conventions in PEP 8 (except for maximum line length, which we don't follow because there are too many parts of the project that require large strings to be used);
-
When writing docstrings, follow the conventions in PEP 257 (take a look at other docstrings in the project to get a feel of how we organize them);
-
Also, when writing docstrings for the API, provide examples of how that method or class works. Having a code example of a part of the API is really helpful for the user.
Developer Setup
Software required in OS:
- Redis Server
- SQLite
- Image Lib
Check out the code from the github project.
git clone git://github.com/opps/opps.git
cd opps
Create a virtualenv (the example here is with virtualenvwrapper) and install all development packages::
mkvirtualenv opps
pip install -r requirements_dev.txt
python setup.py develop
Here is how to run the test suite::
make test
Here is how to build the documentation::
cd docs
make html
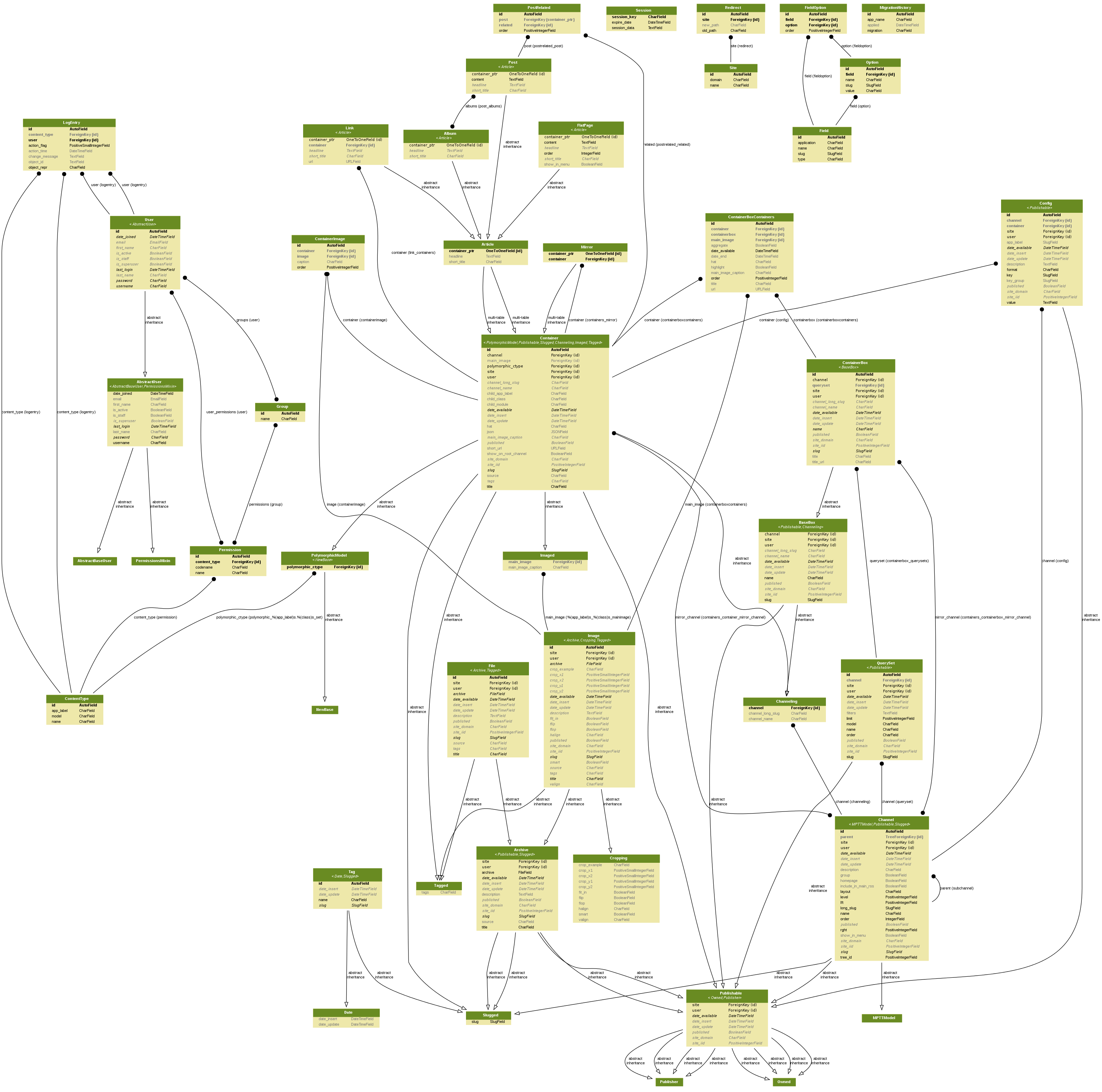
Architecture
South Migrations
Remember this for every South migration created!
For every migration created, make the following modifications.
from django.contrib.auth import get_user_model
User = get_user_model()
class Migration(SchemaMigration):
def forwards(self, orm):
# reapeat the following for every create or alter table using "user" relation
db.create_table('app.model', (
('user', self.gf('django...ForeignKey')(to=orm["%s.%s" % (User._meta.app_label, User._meta.object_name)])
models = {
...
# this should replace "auth.user or accounts.customuser"
"%s.%s" % (User._meta.app_label, User._meta.module_name): {
'Meta': {'object_name': User.__name__},
}
# repeat the following for every freezed model
"app.model": {
'user': ('django.db.models.fields.related.ForeignKey', [], {'to': "orm['%s.%s']"% (User._meta.app_label, User._meta.object_name)})
}
}
Haystack
This is required in order to use the default Haystack setup
The default haystack search template is the same you find in haystack home page, the difference in opps is that for every indexed Model you should implement some fields, properties or methods.
Required for search
- title (The title used on search result)
- search_category (It can be used to group things on tabs or just to show the category)
- get_absolute_url (The url for search result)
- get_thumb (optional image path for search result)
Example
class MyModel(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=255) # implemented as field
slug = models.SlugField()
image = models.FileField()
# implemented as method
def get_absolute_url(self):
return "posts/{0}".format(self.slug)
# implemented as method
def get_thumb(self):
return get_thumb_url_or_something(self.image)
# implemented as property
@property
def search_category(self):
return _(' Blog post')
With the above in your model, you can now create your search_indexes and template and choose to index those fields/properties/methods or just access directly on template. (see haystack docs)
Example of search template
{% load images_tags %}
<h2>Search</h2>
<form method="get" action=".">
<table>
<input type="search" id="q" name="q" placeholder="Search" value="{{ request.GET.q}}" required>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td>
<input type="submit" value="Search">
</td>
</tr>
</table>
{% if query %}
<h3>Results</h3>
{% for result in page.object_list %}
<p>
<small>{{ result.object.search_category }}</small><br>
{% if result.object.get_thumb %}
<a href="{{ result.object.get_absolute_url }}">
<img src="{% image_url result.object.get_thumb.archive.url width=100 height=100 %}" alt="{{ result.object.title}}" class="span2" />
</a>
{% endif %}
<a href="{{ result.object.get_absolute_url }}">{{ result.object.title }}</a>
</p>
{% empty %}
<p>No results found.</p>
{% endfor %}
{% if page.has_previous or page.has_next %}
<div>
{% if page.has_previous %}<a href="?q={{ query }}&page={{ page.previous_page_number }}">{% endif %}« Previous{% if page.has_previous %}</a>{% endif %}
|
{% if page.has_next %}<a href="?q={{ query }}&page={{ page.next_page_number }}">{% endif %}Next »{% if page.has_next %}</a>{% endif %}
</div>
{% endif %}
{% else %}
{# Show some example queries to run, maybe query syntax, something else? #}
{% endif %}
</form>
Running Tests
To run the test you must have an Redis instance running locally on the 6379 port (default one). Then, just type the following
make test
To run tests in multiple python versions, first install tox and then run the tox command:
pip install tox
tox